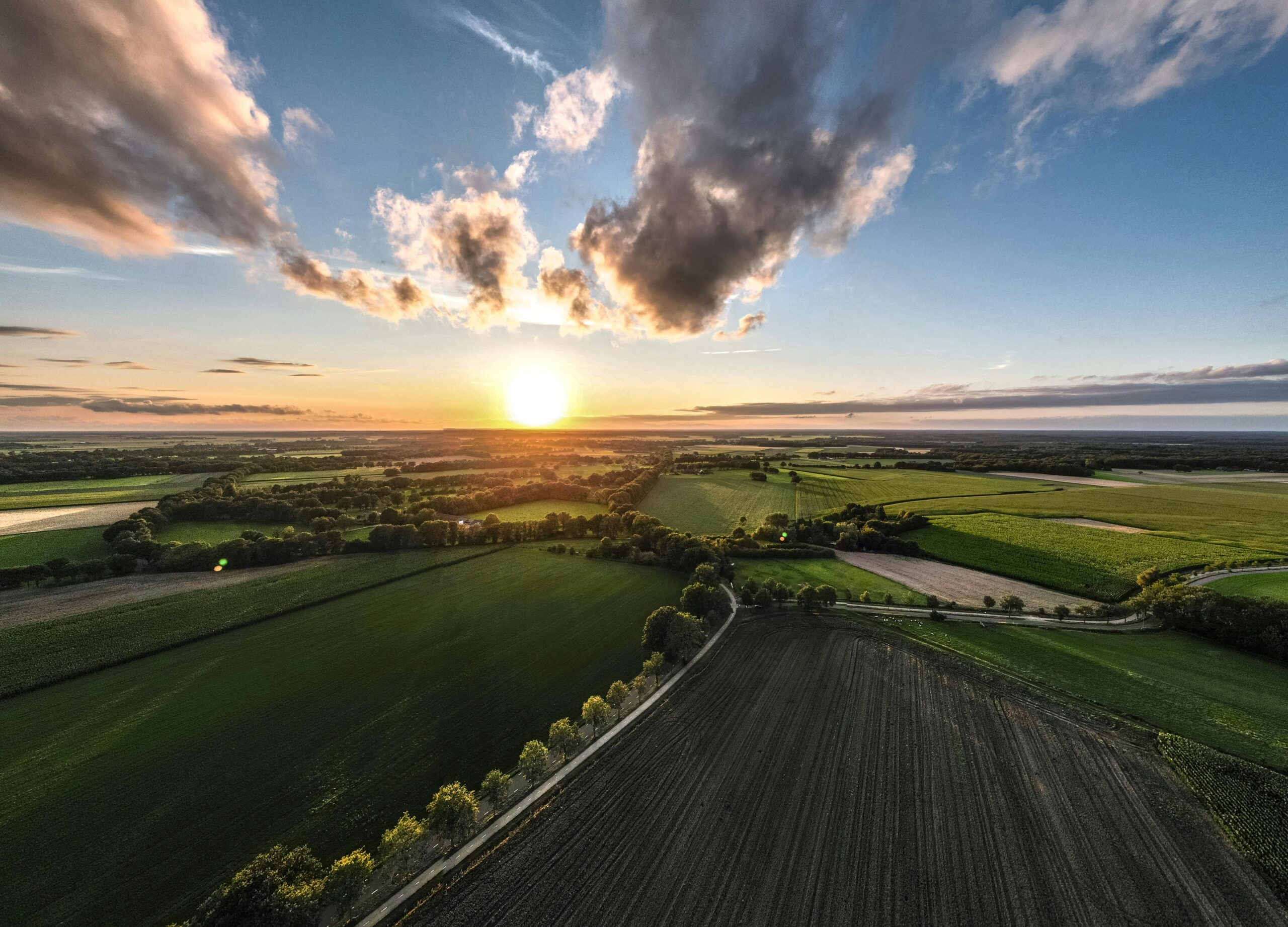

Regenerative agriculture is gaining momentum as a transformative approach to farming, prioritizing soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience.
According to a study published in the journal “Nature Communications,” regenerative agricultural practices have the potential to sequester significant amounts of carbon from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change.
By implementing techniques such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage, regenerative farmers restore soil fertility, enhance water retention, and promote biodiversity, leading to healthier ecosystems and more resilient food systems.
Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring and enhancing the natural processes that sustain healthy ecosystems, rather than depleting them. One of the key principles of regenerative agriculture is soil health, as healthy soils are the foundation of productive and resilient farming systems. By minimizing soil disturbance and maximizing organic matter inputs, regenerative farmers improve soil structure, fertility, and microbial diversity, leading to increased nutrient cycling and water retention.
Cover cropping is a fundamental practice in regenerative agriculture, where farmers plant diverse cover crops between cash crop rotations to protect the soil from erosion, suppress weeds, and enhance soil fertility. Cover crops also provide habitat for beneficial insects and pollinators, further supporting biodiversity on farms.
Crop rotation is another essential component of regenerative agriculture, as it helps break pest and disease cycles, improve soil structure, and replenish soil nutrients. By rotating crops with different nutrient requirements and growth habits, farmers can maintain soil health and productivity over the long term, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Minimal tillage is a key practice in regenerative agriculture, as excessive tillage can disrupt soil structure, increase erosion, and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. By reducing tillage intensity and frequency, regenerative farmers preserve soil structure and organic matter, minimize soil erosion, and sequester carbon in the soil, mitigating climate change.
Regenerative agriculture also emphasizes biodiversity conservation, recognizing the importance of diverse plant and animal species in healthy ecosystems. By incorporating agroforestry, hedgerows, and wildlife corridors into farming landscapes, regenerative farmers create habitat for native species, enhance pollination and pest control services, and promote ecological resilience.
In addition to environmental benefits, regenerative agriculture offers economic advantages for farmers, including reduced input costs, increased resilience to climate variability, and improved market access for sustainably produced products. Consumers are also increasingly demanding ethically and sustainably produced food, driving market demand for regeneratively grown products.
In conclusion, regenerative agriculture offers a holistic and sustainable approach to farming that prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience. As a leading software development company, Coding Brains recognizes the importance of supporting regenerative agriculture initiatives to promote a healthier planet and more sustainable food systems. Through our innovative solutions and partnerships, we are committed to empowering farmers and stakeholders to adopt regenerative practices and build a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.

Leave a Reply