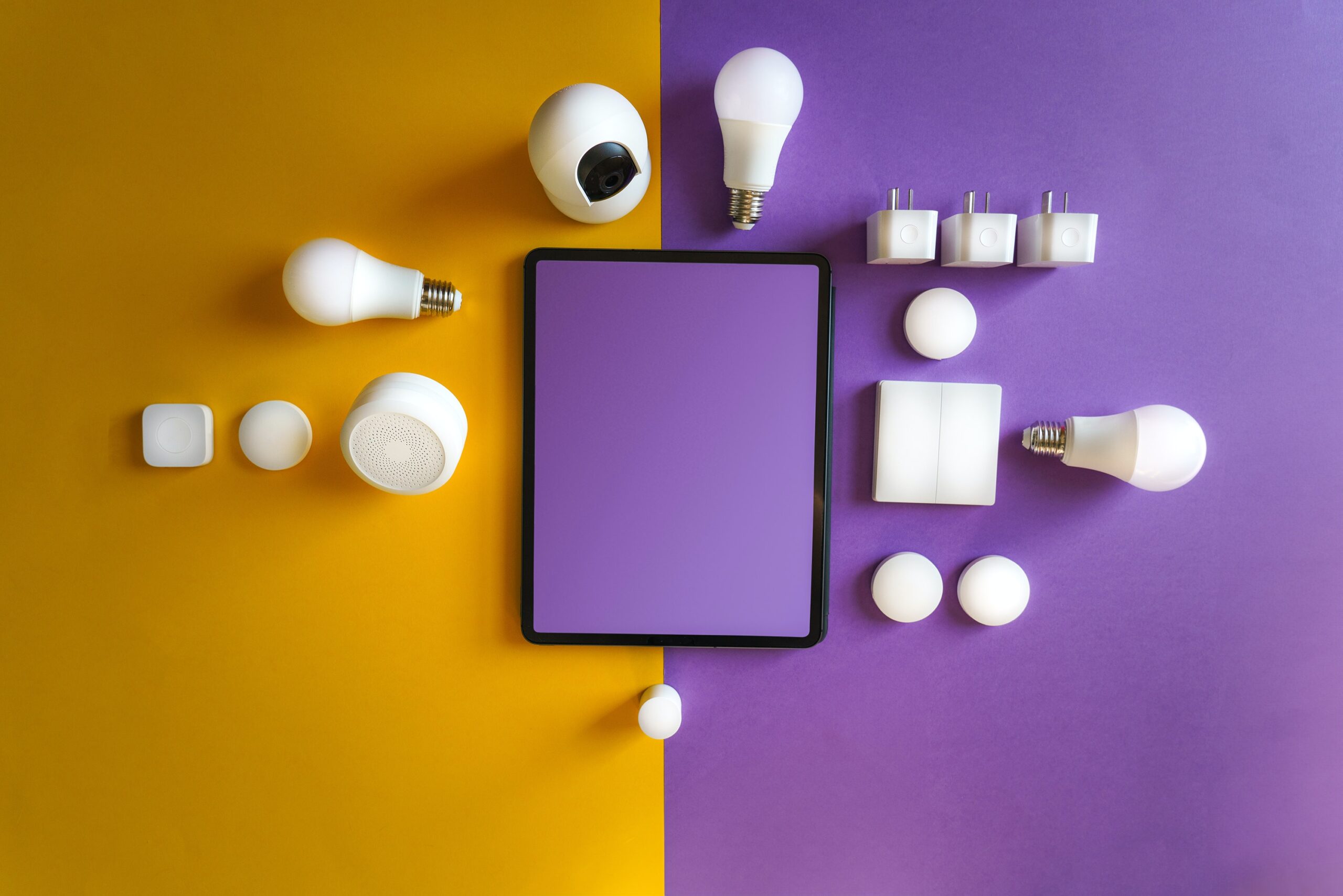

From smart homes to autonomous vehicles, IoT Applications has revolutionized the way we live and work. In today’s hyper-connected world, data is generated at an unprecedented rate. However, this data influx has created significant challenges, including latency and bandwidth issues in centralized cloud computing. Enter edge computing, a game-changing technology that brings data processing closer to the source.
According to recent research by Gartner, by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will be processed at the edge, making it a pivotal aspect of modern computing.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that extends computing resources closer to data sources. Unlike traditional cloud computing, where data travels to a centralized data center for processing, edge computing processes data locally on devices or in nearby data centers. This proximity reduces latency and enhances real-time data processing, making it ideal for IoT Applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
Key Benefits of Edge Computing
Low Latency:
Edge computing significantly reduces data transfer times, making it ideal for IoT Applications requiring real-time decision-making. For example, in autonomous vehicles, split-second decisions can mean the difference between safety and disaster.
Bandwidth Optimization:
By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need for massive data transfers to the cloud, optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing costs.
Improved Privacy and Security:
Sensitive data can be processed and stored locally, reducing the risk of data breaches during transit to the cloud.
Edge Computing in IoT
The IoT ecosystem relies heavily on edge computing to function efficiently. Consider a smart thermostat that needs to adjust the temperature based on user preferences. With edge computing, the thermostat can process data locally, ensuring immediate responses to changing conditions without relying on a distant cloud server. This enhances user experience and system reliability.
Real-world IoT Applications
Autonomous Vehicles:
Edge computing plays a critical role in autonomous vehicles. These vehicles require real-time data processing for navigation, obstacle detection, and collision avoidance. Edge computing allows these operations to happen onboard without the need for continuous cloud connectivity.
Healthcare:
Remote patient monitoring devices, such as wearable health trackers, rely on edge computing for real-time data analysis. This ensures that critical health data is processed promptly and transmitted securely to healthcare providers.
Manufacturing:
Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications in manufacturing leverage edge computing for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. Edge devices collect and analyze data from sensors and machines, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, edge computing is revolutionizing the way we process data and power IoT applications. Its ability to reduce latency, optimize bandwidth, enhance privacy and security, and enable real-time decision-making makes it an indispensable technology in today’s digital landscape. As more industries adopt IoT and demand faster data processing, the role of edge computing will continue to grow.
At Coding Brains, our software development company, we understand the significance of cutting-edge technologies like edge computing. We specialize in developing custom software solutions that harness the power of edge computing to meet the unique needs of our clients. As technology evolves, we remain committed to providing innovative solutions that drive businesses forward in this data-driven world.

Leave a Reply